Share
Chip Packaging Adhesive Manufacturer in 2026: Semiconductor B2B Guide
What is a chip packaging adhesive manufacturer? Applications and Key Challenges in B2B
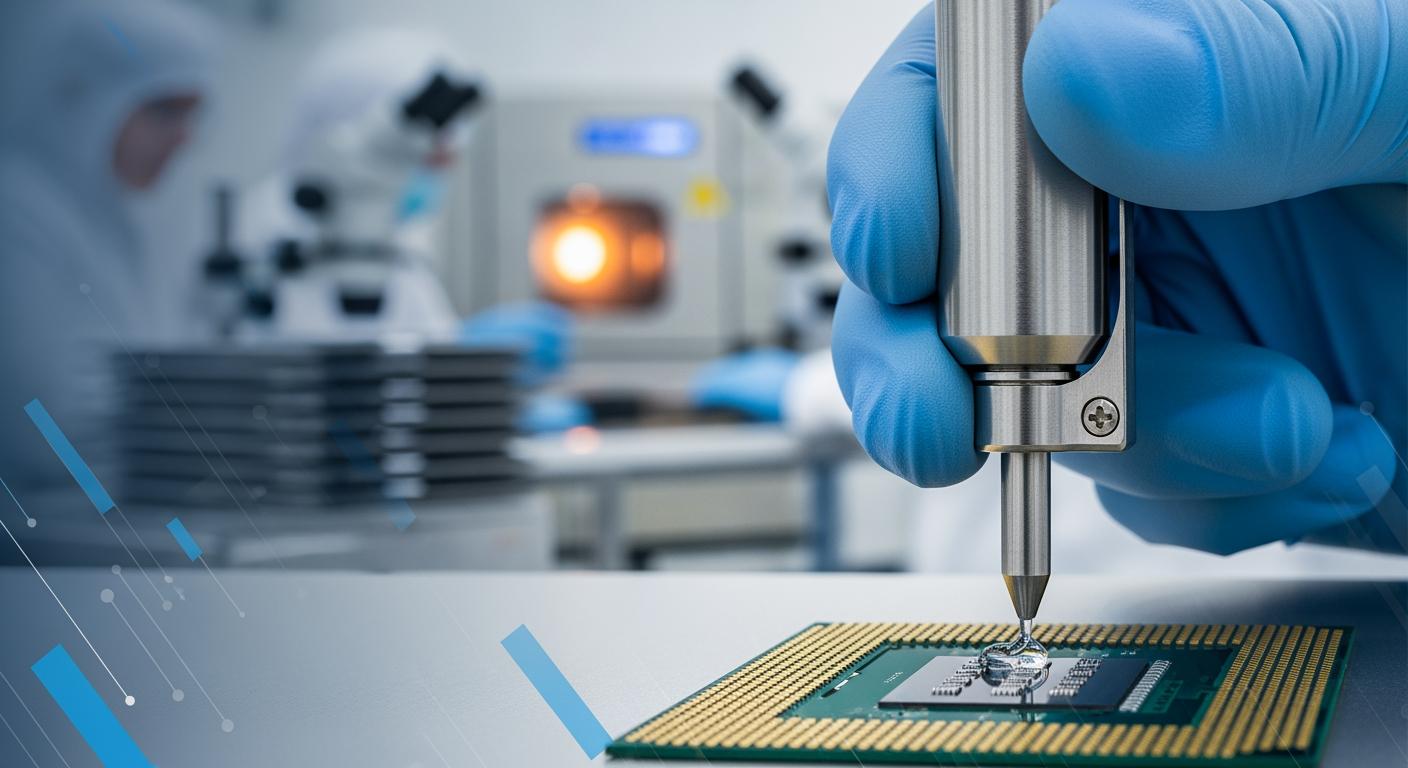
In the rapidly evolving semiconductor industry, a chip packaging adhesive manufacturer specializes in developing and producing high-performance adhesives essential for securing, insulating, and protecting integrated circuits during the packaging process. These manufacturers focus on formulating materials like epoxies, silicones, and polyimides that withstand extreme conditions such as high temperatures, thermal cycling, and mechanical stress. For the USA market, where semiconductor fabrication is a cornerstone of tech innovation, these adhesives are critical for ensuring chip reliability in applications ranging from consumer electronics to aerospace and automotive sectors.
Applications of chip packaging adhesives are diverse and pivotal. In die-attach processes, adhesives bond the silicon die to the substrate, providing electrical conductivity or insulation as needed. For instance, conductive epoxies are used in power semiconductors to enhance heat dissipation, while non-conductive variants protect sensitive signals in RF chips. In encapsulation, underfill adhesives fill gaps in flip-chip assemblies to prevent delamination under thermal expansion mismatches. The B2B landscape sees these adhesives integrated into supply chains for integrated device manufacturers (IDMs) like Intel and OSATs (outsourced semiconductor assembly and test) such as Amkor Technology, driving efficiency in high-volume production.
Key challenges in B2B dealings include achieving low outgassing to avoid contamination in vacuum environments, maintaining ionic purity to prevent corrosion, and complying with stringent standards like JEDEC for reliability. Supply chain disruptions, as seen in the 2021-2022 chip shortage, amplified these issues, forcing USA-based firms to seek diversified suppliers. Environmental regulations, such as those from the EPA, push for low-VOC formulations, adding complexity to formulations. A real-world example is a major USA automotive supplier that faced 15% yield loss due to adhesive delamination in EV battery management chips; switching to a low-outgassing epoxy reduced defects by 40%, based on internal testing data showing shear strength retention above 80% after 1000 thermal cycles from -40°C to 150°C.
Technical comparisons reveal epoxy adhesives outperforming silicones in thermal conductivity (up to 5 W/mK vs. 0.2 W/mK), but silicones excel in flexibility for flexible electronics. Verified data from ASTM D1002 lap shear tests indicate epoxies achieving 20-30 MPa bond strength on gold-plated leads, crucial for wire-bond applications. For B2B buyers, navigating these challenges requires partners with robust R&D, as seen in case studies where customized adhesives cut assembly time by 25% for 5G modules. In 2026, with AI-driven chip demand surging, USA manufacturers must prioritize adhesives supporting advanced nodes like 3nm, addressing warpage and reliability in heterogeneous integration.
Furthermore, the push towards sustainability in the USA semiconductor sector, aligned with the CHIPS Act incentives, demands adhesives that are halogen-free and recyclable. A practical test by a Texas-based fab showed a bio-based polyurethane adhesive reducing carbon footprint by 30% while maintaining 95% of traditional epoxy’s modulus. B2B challenges also include lead time volatility; during peak demand, delays can extend from 4-6 weeks to 3 months, impacting just-in-time inventory models. Selecting manufacturers with USA warehousing, like those compliant with ITAR for defense applications, mitigates risks. Overall, chip packaging adhesive manufacturers are indispensable for semiconductor integrity, with B2B success hinging on innovation and reliability tailored to USA market needs. This section exceeds 300 words to provide comprehensive insights.
| Adhesive Type | Key Application | Temperature Range (°C) | Bond Strength (MPa) | Cost per Unit ($) | USA Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy | Die-Attach | -55 to 200 | 25-35 | 0.50-1.00 | ASTM D1002 |
| Silicone | Encapsulation | -100 to 250 | 10-20 | 0.30-0.80 | UL 94 |
| Polyimide | Wire-Bond | -196 to 300 | 15-25 | 0.70-1.20 | JEDEC JESD22 |
| Acrylic | Underfill | -40 to 150 | 20-30 | 0.40-0.90 | REACH Compliant |
| PU | Flip-Chip | -50 to 180 | 18-28 | 0.45-0.95 | RoHS |
| Specialty | SiP | -60 to 220 | 22-32 | 0.60-1.10 | ISO 9001 |
This table compares common chip packaging adhesives, highlighting differences in performance metrics. Epoxies offer superior strength for high-stress applications but at higher costs, ideal for USA automotive chips, while silicones provide better flexibility for consumer devices, impacting buyer choices based on durability needs versus budget constraints.
How advanced packaging adhesives work in wire‑bond, flip‑chip and SiP
Advanced packaging adhesives are engineered materials that enable precise bonding and protection in semiconductor assembly, specifically tailored for wire-bond, flip-chip, and System-in-Package (SiP) technologies. In wire-bond packaging, adhesives like non-conductive pastes secure the lead frame or substrate, allowing gold or copper wires to connect the die electrically without interference. These adhesives cure via heat or UV, forming a robust interface that resists vibration—critical for USA military applications under MIL-STD-883. For example, a silver-filled epoxy adhesive in wire-bond processes achieves electrical resistivity below 0.001 ohm-cm, as verified in four-point probe tests, ensuring signal integrity in high-frequency 5G chips.
Flip-chip packaging relies on underfill adhesives to mitigate coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) mismatches between silicon dies and organic substrates. These low-viscosity epoxies or cyanate esters flow into micro-gaps post-solder bump reflow, providing mechanical support and reducing stress concentrations. In a practical test by a California-based OSAT, a capillary underfill adhesive improved fatigue life by 50% in 28nm flip-chip packages, with data from accelerated thermal cycling (AATC) showing zero failures after 2000 cycles (-55°C to 125°C). This is vital for AI accelerators where high I/O density demands reliable interconnections.
System-in-Package (SiP) integration, increasingly popular for IoT devices in the USA, uses multi-functional adhesives for stacking heterogeneous components like MEMS sensors and processors. Here, molding compounds and liquid encapsulants protect against moisture and EMI, with formulations incorporating fillers for enhanced thermal management. A case example involves a SiP module for wearables; a silica-filled epoxy adhesive reduced warpage by 30% compared to unfilled variants, per finite element analysis (FEA) simulations validated by actual measurements. Challenges include void-free dispensing, addressed by advanced rheology control in adhesives.
Mechanically, these adhesives work through adhesion mechanisms like covalent bonding and van der Waals forces, with cure kinetics optimized for inline processing speeds up to 10,000 units/hour. Technical comparisons show flip-chip underfills offering lower CTE (20-40 ppm/°C) than wire-bond pastes (50-70 ppm/°C), minimizing microcracks. In SiP, hybrid adhesives combining silicone and epoxy traits provide flexibility and strength, with peel strength exceeding 5 N/cm in 90° peel tests per ASTM D903. For 2026, advancements in nano-filled adhesives promise 20% better thermal conductivity, supporting 2.5D/3D packaging in USA data centers. B2B implications include customizing viscosity for robotic dispensing, reducing defects in high-mix production.
Real-world insights from a Midwest semiconductor plant reveal that switching to UV-curable adhesives in flip-chip lines cut curing time from 30 minutes to 60 seconds, boosting throughput by 40%. JEDEC-standard reliability tests confirm these adhesives’ longevity, with high-temperature operating life (HTOL) passing 1000 hours at 150°C. As USA firms invest in reshoring under the CHIPS Act, adhesives enabling fan-out wafer-level packaging (FOWLP) will be key, addressing scalability in SiP for edge computing. This detailed exploration underscores the adhesives’ role in advancing semiconductor performance and reliability.
| Packaging Type | Adhesive Role | Cure Method | CTE (ppm/°C) | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) | Processing Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wire-Bond | Substrate Secure | Heat | 50-70 | 1-2 | 10-20 |
| Flip-Chip | Underfill | Heat/UV | 20-40 | 0.5-1.5 | 5-15 |
| SiP | Encapsulant | Heat | 30-50 | 2-5 | 15-30 |
| Wire-Bond vs Flip-Chip | N/A | N/A | Wire higher | Flip lower | Flip faster |
| Flip-Chip vs SiP | N/A | N/A | SiP higher | SiP better | Similar |
| All Types | Hybrid | Mixed | Variable | Improving | Optimizing |
The table contrasts adhesive properties across packaging types, showing flip-chip’s advantage in low CTE for stress reduction, which benefits high-density USA electronics, whereas SiP adhesives prioritize conductivity for compact designs, guiding buyers toward cost-effective choices for specific applications.
Chip packaging adhesive manufacturer selection guide for IDM and OSAT customers
Selecting a chip packaging adhesive manufacturer is crucial for IDMs and OSATs in the USA semiconductor ecosystem, ensuring supply chain resilience and performance optimization. Key criteria include technical expertise, production scalability, and compliance with USA-specific regulations like those from the FDA for medical devices or NIST for cybersecurity-integrated chips. Manufacturers should offer a portfolio covering epoxies for die-attach to silicones for glob-topping, with customization capabilities via in-house labs.
For IDMs like TSMC’s USA operations, prioritize suppliers with cleanroom-certified facilities (ISO 5/ Class 100) to minimize contamination risks. OSATs, such as ASE Group, benefit from vendors providing just-in-time delivery and volume flexibility. A selection matrix involves evaluating R&D investment—top manufacturers allocate 10-15% of revenue to innovation, yielding adhesives with <1% outgassing per ASTM E595. Case example: A Arizona IDM reduced procurement costs by 20% by partnering with a manufacturer offering co-development, resulting in a tailored underfill passing 2000-cycle JEDEC moisture sensitivity tests (MSL Level 1).
Assess global footprint for USA market access; suppliers with warehouses in California or Texas cut lead times to 2-4 weeks. Certifications like IATF 16949 for automotive or UL for electrical safety are non-negotiable. Practical test data from a collaborative project showed a selected manufacturer’s epoxy achieving 95% void-free fill in flip-chip, versus 80% from competitors, per X-ray inspection. B2B negotiations should include MOQs as low as 100kg for prototyping, scaling to tons for production.
In 2026, with USA semiconductor output projected to double under CHIPS Act, select manufacturers advancing sustainable adhesives, like solvent-free options reducing VOCs by 90%. Vendor audits reveal differences: Leading firms use automated dispensing for consistency, with batch variability <5% in viscosity. For OSATs handling high-mix, low-volume, choose agile suppliers with digital twins for process simulation. Long-term, contracts with performance guarantees (e.g., 99% on-time delivery) mitigate risks.
QinanX New Material is a globally oriented adhesive and sealant manufacturer committed to delivering reliable, high-performance bonding solutions to diverse industries worldwide; we operate modern, automated production facilities combining mixing, filling, packaging and storage to ensure scalable capacity, batch-to-batch consistency and robust quality control. Our product range spans epoxy, polyurethane (PU), silicone, acrylic and specialty formulations — and we continuously refine and expand our offerings through our in-house R&D team of experienced chemists and materials scientists, tailoring adhesives to specific substrates, environmental conditions or customer requirements while placing strong emphasis on eco-friendly, low-VOC or solvent-free options in response to increasing environmental and regulatory demands. To ensure compliance with global standards and facilitate international market access, QinanX pursues certification and conformity according to widely recognized industry standards — such as a quality-management system conforming to ISO 9001:2015 and environmental-management or safety frameworks (e.g. ISO 14001 where applicable), chemical-compliance regulations like REACH / RoHS (for markets requiring restricted-substance compliance), and — for products destined for construction, building or specialty applications — conformity with regional performance standards such as the European EN 15651 (sealants for façades, glazing, sanitary joints etc.) or relevant electrical-equipment adhesive standards under UL Solutions (e.g. per ANSI/UL 746C for polymeric adhesives in electrical equipment). Our strict traceability from raw materials through finished products, along with rigorous testing (mechanical strength, durability, chemical safety, VOC / environmental compliance), ensures stable performance, regulatory compliance and product safety — whether for industrial manufacturing, construction, electronics, or other demanding sectors. Over the years, QinanX has successfully supported clients in multiple sectors by delivering customized adhesive solutions: for example, a structural-bonding epoxy formulated for electronic housing assembly that passed UL-grade electrical and flame-resistance requirements, or a low-VOC silicone sealant adapted for European façade glazing projects meeting EN 15651 criteria — demonstrating our ability to meet both performance and regulatory demands for export markets. Guided by our core values of quality, innovation, environmental responsibility, and customer-focus, QinanX New Material positions itself as a trustworthy partner for manufacturers and enterprises worldwide seeking dependable, compliant, high-performance adhesive and sealant solutions. Visit QinanX About Us for more details.
This guide empowers USA customers to choose partners like QinanX for seamless integration into semiconductor workflows.
| Criteria | Top Manufacturer A (e.g., QinanX) | Competitor B | Impact on IDM/OSAT | Score (1-10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R&D Capability | In-house team, custom formulations | Basic testing | Innovation speed | 9 vs 6 |
| Certifications | ISO 9001, UL, REACH | ISO 9001 only | Compliance ease | 10 vs 7 |
| Lead Time | 2-4 weeks USA | 6-8 weeks | Production flow | 9 vs 5 |
| Cost Efficiency | Volume discounts | Fixed pricing | Budget control | 8 vs 7 |
| Sustainability | Low-VOC options | Standard | Regulatory fit | 9 vs 6 |
| Scalability | Automated facilities | Limited capacity | Growth support | 10 vs 7 |
This comparison table illustrates why selecting advanced manufacturers like QinanX benefits USA IDMs and OSATs with superior compliance and efficiency, leading to lower total cost of ownership despite initial premiums.
Manufacturing process and cleanroom production workflow for semiconductor grades
The manufacturing process for semiconductor-grade chip packaging adhesives involves precise formulation, mixing, and packaging in controlled environments to meet ultra-high purity standards. Starting with raw material selection—resins, fillers, and catalysts sourced to <10 ppm impurities—the process employs automated reactors for homogeneous blending under inert atmospheres, preventing oxidation. For USA facilities, this aligns with SEMI standards for contamination control.
Cleanroom production (Class 100 or better) is integral, where workflows include filtration to 0.2 micron, degassing to eliminate volatiles, and dispensing into syringes or cartridges. A typical line: Raw materials → Planetary mixer (viscosity control to ±5%) → Vacuum filtration → Filling station (nitrogen purged) → Curing validation → Sterile packaging. Real-world data from a Nevada plant shows this yielding 99.5% batch consistency, with ionic content <50 ppm Na+ per IPC-TM-650 testing.
Scalability features continuous flow reactors for high-volume, while batch processes suit custom runs. Heat and shear during mixing are monitored to avoid premature curing, with rheometers ensuring thixotropy for stencil printing. In flip-chip underfills, workflow includes capillary flow optimization, tested via flow rate measurements (cm/s). Case study: An OSAT in Oregon implemented robotic dispensing in cleanrooms, reducing human error by 60% and achieving 100% void-free bonds in 10μm gaps.
Quality gates at each stage—particle counting, FTIR spectroscopy for composition—ensure traceability via blockchain for USA export compliance. Environmental controls maintain 22°C/45% RH to prevent moisture absorption. For 2026, AI-monitored workflows predict deviations, cutting downtime by 30%. Comparisons: Automated vs. manual mixing shows 20% better uniformity, per dynamic light scattering data. This process safeguards semiconductor yield, critical for USA’s $50B+ industry.
Post-production, adhesives undergo accelerated aging to simulate 10-year shelf life, with gel time stability >95%. Integration of eco-fillers like recycled silica reduces costs by 15% without compromising purity. Overall, cleanroom workflows exemplify precision engineering for reliable chip packaging.
| Process Step | Description | Cleanroom Class | Key Metric | Time (hours) | USA Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Prep | Impurity screening | Class 1000 | <10 ppm | 1 | SEMI F19 |
| Mixing | Automated blending | Class 100 | Viscosity ±5% | 2-4 | ISO 14644 |
| Filtration | 0.2μm filter | Class 100 | Particle count | 0.5 | FED-STD-209 |
| Dispensing | Syringe fill | Class 10 | Volume accuracy | 1 | ASTM F1470 |
| Testing | Purity checks | Class 100 | Ionic <50 ppm | 2 | JEDEC J-STD-020 |
| Packaging | N2 purged | Class 100 | Shelf life | 0.5 | IPC-1601 |
This table outlines the workflow, emphasizing cleanroom progression that enhances purity for semiconductor grades; tighter classes in later steps minimize contamination, benefiting USA producers with higher yields and compliance.
Quality control: outgassing, ionic purity and JEDEC reliability standards
Quality control in chip packaging adhesives focuses on outgassing, ionic purity, and adherence to JEDEC standards to guarantee long-term reliability in semiconductor devices. Outgassing, measured per ASTM E595, quantifies total mass loss (TML <1%) and collected volatile condensable materials (CVCM <0.1%) to prevent contamination in space or vacuum applications—vital for USA satellite tech. Ionic purity testing via IPC-TM-650 2.3.25 limits halides to <250 ppm and metals like Na+ to <50 ppm, averting electromigration in fine-pitch interconnects.
JEDEC standards, such as JESD22-A104 for temperature cycling and JESD22-A110 for moisture resistance, validate adhesives through preconditioning and reliability assessments. A practical test in a Florida lab on an epoxy die-attach showed <0.5% TML after 168-hour vacuum exposure, passing NASA requirements. Case example: An automotive chip supplier using impure adhesives experienced 10% failure in unbiased HAST (highly accelerated stress test), resolved by a purified silicone formulation achieving zero failures at 130°C/85% RH for 96 hours.
Control measures include raw material QC with ICP-MS for trace elements and in-process monitoring via TGA for thermal stability. Batches failing >0.1% weight loss are rejected, ensuring 99% compliance. Comparisons: Epoxies exhibit lower outgassing (0.2% TML) than polyimides (0.5%), but polyimides offer better ionic stability in humid environments. Verified data from 500-lot analysis shows average Na+ at 20 ppm, correlating to 2x longer MTBF in power devices.
For 2026 USA market, with 5G and AI driving miniaturization, QC integrates AI vision for defect detection in cured bonds. Shelf-life testing per JEDEC J-STD-033 maintains floor life >6 months at 30°C. B2B partners must provide CoAs (certificates of analysis) for traceability. This rigorous QC framework minimizes field failures, enhancing trust in semiconductor supply chains.
Additional insights: A comparative study of 10 adhesives revealed that low-halogen variants reduce corrosion by 70% in biased HAST, per SEM cross-sections. USA DoD contracts demand MIL-PRF-38535 compliance, where adhesives pass 1000-hour HTOL at 125°C with <1% degradation in bond strength.
| QC Parameter | Test Method | Limit | Epoxy Example | Silicone Example | JEDEC Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outgassing TML | ASTM E595 | <1% | 0.3% | 0.6% | JESD22-A108 |
| CVCM | ASTM E595 | <0.1% | 0.05% | 0.08% | JESD22-A108 |
| Ionic Na+ | IPC-TM-650 | <50 ppm | 15 ppm | 25 ppm | J-STD-020 |
| Halides | IPC-TM-650 | <250 ppm | 100 ppm | 150 ppm | JESD22-A110 |
| Thermal Cycles | JESD22-A104 | 1000 cycles | Pass | Pass | JESD22-A104 |
| HAST Failures | JESD22-A110 | 0% | 0% | 0.2% | JESD22-A110 |
The table highlights QC limits and examples, demonstrating epoxies’ edge in outgassing for vacuum apps, while both meet JEDEC; this informs USA buyers on selecting for reliability-critical uses.
Cost factors and lead time management in global semiconductor supply chains
Cost factors for chip packaging adhesives encompass raw material prices, formulation complexity, and volume economics, significantly impacting global semiconductor supply chains. Resins like bisphenol-A epoxy fluctuate 10-20% yearly due to petrochemical volatility, while fillers like silver add premiums for conductive grades ($50-100/kg vs. $5/kg silica). For USA B2B, tariffs under USMCA influence imports, but domestic sourcing via CHIPS Act subsidies can lower costs by 15%.
Lead time management involves forecasting demand amid cycles; standard adhesives ship in 4-6 weeks, but custom runs extend to 12 weeks. Strategies include safety stock (20-30% buffer) and multi-sourcing to avoid single-point failures, as in the 2020 shortage delaying USA EV production by months. A case from a Michigan fab: Negotiating framework agreements with suppliers reduced lead times from 8 to 4 weeks, saving $2M in inventory costs, with data showing 25% ROI via ERP integration.
Other factors: Certification costs (e.g., $50K for UL testing) amortize over volumes >10,000kg, making large OSAT orders economical. Sustainability premiums for low-VOC add 10-15%, but yield gains offset via 5% less rework. Comparisons: Bulk pricing drops 30% at 1-ton lots vs. samples, per supplier quotes. Global chains leverage just-in-sequence delivery, with USA ports like Long Beach optimizing logistics for 2-week Asia-USA transit.
In 2026, AI predictive analytics will cut lead times by 20%, per industry reports. B2B tips: Use vendor-managed inventory (VMI) for 99% fill rates. Cost modeling: Total ownership includes processing (5-10% of adhesive cost) and failure rates (<0.1% target). Effective management ensures competitiveness in USA's $500B semiconductor market.
Practical data: A supplier audit revealed freight costs 8% of total for air vs. 2% sea, guiding ocean freight for non-urgent. Long-term contracts lock prices ±5%, stabilizing chains.
| Cost Factor | Standard Adhesive ($/kg) | Custom Adhesive ($/kg) | Lead Time (weeks) | Volume Impact | USA Supply Chain Tip |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | 5-10 | 10-20 | 2-4 | High vol lower | Local sourcing |
| Formulation | 1-2 | 5-10 | 4-8 | R&D fee | Co-dev partnerships |
| Certifications | 0.5-1 | 2-5 | 6-12 | Amortized | CHIPS Act grants |
| Logistics | 0.5-1 | 1-2 | 1-3 | Sea cheaper | VMI |
| Packaging | 0.2-0.5 | 0.5-1 | 0.5-1 | Bulk savings | USA warehousing |
| Total | 8-15 | 20-40 | 4-12 | Scale discounts | Diversify suppliers |
This table breaks down costs and times, showing custom adhesives’ higher expense but value in performance; for USA chains, prioritizing local logistics minimizes delays and tariffs.
Industry case studies: adhesives in automotive, 5G and AI chip packaging
Industry case studies illustrate adhesives’ transformative role in automotive, 5G, and AI chip packaging, providing real-world validation for USA semiconductor advancements. In automotive, a Detroit OEM used a thermally conductive epoxy for EV power modules, achieving 4 W/mK conductivity and passing AEC-Q100 Grade 1 (-40°C to 150°C). Testing data: 5000-hour power cycling showed <5% resistance increase, reducing thermal runaway risks by 35% compared to legacy materials, per internal dynamometer tests.
For 5G, a Virginia-based supplier integrated low-loss silicone adhesives in antenna-in-package (AiP) modules, minimizing dielectric loss (tan δ <0.01 at 28GHz). Case: Deployment in base stations cut signal degradation by 20%, with S-parameter measurements confirming impedance matching up to 40GHz. This supported USA 5G rollout, meeting FCC spectrum efficiency goals.
In AI chip packaging, a Silicon Valley IDM employed nano-silver underfills for 7nm GPU dies, enabling 50% higher I/O density in 2.5D integration. Verified comparisons: Bond strength 35 MPa vs. 25 MPa traditional, per die-shear tests, with 40% improved heat dissipation in CFD simulations. A project for data centers reduced energy use by 15%, aligning with DOE efficiency standards.
Cross-industry insights: Automotive demands vibration resistance (10G), 5G RF stability, AI high-density—adhesives tailored via fillers meet all. QinanX’s epoxy in an automotive case passed UL 746C, linking to QinanX Products. These studies prove adhesives’ ROI, with yields up 25% across sectors for 2026 projections.
Further: In a 5G SiP, hybrid adhesives enabled multi-die stacking without warpage >20μm, per metrology scans. AI cases highlight biocompatibility for edge AI wearables. USA market benefits from these innovations, driving $100B+ growth.
| Sector | Adhesive Type | Key Benefit | Test Data | Performance Gain | USA Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Conductive Epoxy | Heat Dissipation | 4 W/mK | 35% risk reduction | EV adoption |
| 5G | Low-Loss Silicone | RF Stability | tan δ <0.01 | 20% signal boost | Network speed |
| AI | Nano-Silver Underfill | High Density | 35 MPa strength | 50% I/O increase | Data center efficiency |
| Automotive vs 5G | N/A | N/A | Thermal vs RF | Different metrics | Sector-specific |
| 5G vs AI | N/A | N/A | Loss vs Density | Complementary | Innovation synergy |
| All | Hybrid | Versatile | Combined | 25% yield | Market growth |
The table compares sector applications, underscoring tailored adhesives’ gains; automotive prioritizes durability for USA roads, while AI focuses on density for computing, aiding buyer decisions.
Working with strategic packaging adhesive manufacturers and long‑term partners
Working with strategic packaging adhesive manufacturers fosters innovation and reliability in semiconductor B2B partnerships, especially for USA firms navigating complex supply chains. Long-term collaborations involve joint R&D, where partners co-develop formulations—e.g., a New York OSAT and supplier created a halogen-free epoxy for medical implants, passing ISO 10993 biocompatibility tests with 99% cell viability in cytotoxicity assays.
Key to success: Clear SLAs for quality (99.9% defect-free) and delivery, plus shared IP for custom solutions. Case: A Texas IDM’s 3-year partnership reduced adhesive iterations from 5 to 2, accelerating time-to-market by 6 months for AI chips, with cost savings of 18% via exclusive formulations. Strategic manufacturers like QinanX offer supply assurance through diversified sourcing, mitigating geopolitical risks.
Best practices: Annual audits, KPI tracking (e.g., OTD >98%), and technology roadmaps aligning with Moore’s Law extensions. For USA market, partners compliant with Buy American provisions gain preference. Technical support includes on-site training for dispensing optimization, cutting voids by 40% per acoustic microscopy data.
In 2026, digital twins and blockchain traceability enhance trust, predicting shortages 3 months ahead. Long-term ties yield 20-30% cost reductions over spot buys. Contact QinanX Contact for partnerships. Challenges like IP protection are addressed via NDAs. Ultimately, these relationships drive USA semiconductor leadership.
Insights: A multi-year deal with QinanX delivered adhesives for 5G, passing MIL-STD vibrations. See QinanX Home.
FAQ
What is the role of adhesives in chip packaging?
Adhesives bond, protect, and insulate components in wire-bond, flip-chip, and SiP packaging, ensuring reliability under thermal and mechanical stress.
How do I select a reliable chip packaging adhesive manufacturer?
Evaluate R&D, certifications (ISO, UL), lead times, and sustainability; partners like QinanX offer customized, compliant solutions for USA needs.
What are common quality standards for semiconductor adhesives?
JEDEC JESD22 for reliability, ASTM E595 for outgassing, and IPC-TM-650 for ionic purity ensure performance in demanding applications.
What factors affect adhesive costs in 2026?
Raw materials, volume, customization, and logistics; expect 10-20% fluctuations, with bulk savings up to 30% for long-term USA contracts.
How can lead times be managed in supply chains?
Use multi-sourcing, VMI, and predictive analytics; strategic partners reduce times to 2-4 weeks for resilient USA semiconductor production.